 Arthroplasty literally means a surgical repair of a joint. It is an operative procedure done by an orthopedic surgeon who replaces or repairs a dysfunctional joint. In many cases these joints have been damaged through either injury or the long term degeneration of an arthritic condition. Arthritis is really a generic term that describes over 100 different medical conditions that affect the musculoskeletal system. In some severe cases, where the joints have been disabled and the individual is no longer able to be functional, arthroplasty surgery is recommended.
Arthroplasty literally means a surgical repair of a joint. It is an operative procedure done by an orthopedic surgeon who replaces or repairs a dysfunctional joint. In many cases these joints have been damaged through either injury or the long term degeneration of an arthritic condition. Arthritis is really a generic term that describes over 100 different medical conditions that affect the musculoskeletal system. In some severe cases, where the joints have been disabled and the individual is no longer able to be functional, arthroplasty surgery is recommended.
Currently there are forms of arthroplasty which include re-sectioning the joint structure, resurfacing the joint structure and replacing the joint structure. For the last 45 years the most common form has been a surgical replacement with a prosthetic. The most common form of arthroplasty is replacement of the hip, knee and hands. Other indications for arthroplasty include a vascular necrosis, congenital dyslocation, traumatized joints and rheumatoid arthritis. (1)
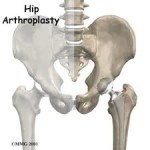
The purpose of any arthroplasty surgery is to relieve the pain and restore range of motion to the individual. Many times this means improved ability to walk, improved muscle strength or improved ability to use their hands.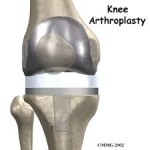
While a total hip replacement or a total knee replacement has been practiced for decades it is only been in the last 10 years that researchers have made technological improvements in the joint replacements in order to both increase the lifespan of the prosthetic and decrease the risk to the individual following the surgery.
 For instance, significant advances have occurred in a total knee replacement as to the type and quality of the materials used. Most recently manufacturers have begun using ceramics which leads to improve longevity of the joints. The primary indication for a total knee arthroplasty is to relieve pain and improve functionality. Correction of a significant deformity may be an indication that is rarely the primary indication for surgery. Prior to considering any arthroplasty surgery orthopedic surgeons must exhaust all conservative treatment measures.
For instance, significant advances have occurred in a total knee replacement as to the type and quality of the materials used. Most recently manufacturers have begun using ceramics which leads to improve longevity of the joints. The primary indication for a total knee arthroplasty is to relieve pain and improve functionality. Correction of a significant deformity may be an indication that is rarely the primary indication for surgery. Prior to considering any arthroplasty surgery orthopedic surgeons must exhaust all conservative treatment measures.
More recently, resurfacing arthroplastic surgical procedures have been developed which are a temporary fix for an individual who has significant degenerative joint disease. This procedure has been used in order to increase the length of time an individual may be functional. For instance, the average lifespan of a total hip replacement is 20 years for the prosthetic joints. (2)
References:
(1) MayoClinic.com: Hip Resurfacing
http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/hip-resurfacing/AN01550
(2) TriRivers Surgical Associates :Understanding Joint Resurfacing
http://www.tririversortho.com/uploaded/pdf/142753_JointResurfacing.pdf
Resources:
Radiographics: Joint Arthroplasties and Prostheses
http://radiographics.rsna.org/content/23/5/1295.full
Acta Orthopaedica: C-Reactive Protein Levels After 4 types of Arthroplasty
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2823221/
American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons: Wrist Joint Replacement
http://orthoinfo.aaos.org/topic.cfm?topic=A00019

Leave a Reply