 Anti-oxidants work in a specific manner to alleviate the damage done by free radicals in the body. These free radicals happened in 1% or 2% of cells that get damaged in the process of oxidation. The term “free” is used because they are missing a critical molecule which sends them on a rampage to find their missing part.
Anti-oxidants work in a specific manner to alleviate the damage done by free radicals in the body. These free radicals happened in 1% or 2% of cells that get damaged in the process of oxidation. The term “free” is used because they are missing a critical molecule which sends them on a rampage to find their missing part.
The danger is not that a free radical will simply kill a cell. The problem is that they injure the cells and damage DNA. When a cell’s DNA changes it mutates and can grow abnormally, reproducing quickly and abnormally. Normal cell function inside the body often produces a small percentage of free radicals but these are generally not a large problem. It is the external toxins which we breathe in, pesticides, alcohol, tobacco and pollution which triggers substantial free radical production and damage.
This damage will set off a chain reaction within the body. This can overwhelm the body’s natural defense system and, with repeated attacks, damage can lead to a host of chronic illnesses. Oxidative damage in skin cells is caused by the cumulative effect of ultraviolet rays. This is called photo aging and often results in brown spots or “liver spots”. However, if the free radicals occur in an internal organ it stimulates reactions in those tissues.
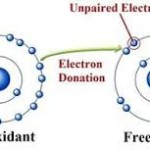
Antioxidants work by blocking the process of oxidation. In fact they neutralize free radicals, which is why there is a constant need to replenish these resources in the body. They work in one of two ways. In the first case, the free radical releases or steals an electron and then a second free radical is formed. This second molecule turns around and does the same thing to another molecule which continues to generate more unstable molecules in a very quick process. The process stops when the molecule is stabilized by a chain breaking antioxidant or simply decays into a harmless chemical.
| Advertisement | |
 |
|

Leave a Reply