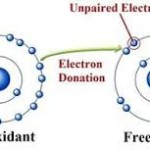
 In the second case, the antioxidant prevents oxidation by reducing the rate of initiation. They scavenged free radicals and can stop the chain formation from ever being set in motion. These are often antioxidant enzymes such as catalase and glutathione.
In the second case, the antioxidant prevents oxidation by reducing the rate of initiation. They scavenged free radicals and can stop the chain formation from ever being set in motion. These are often antioxidant enzymes such as catalase and glutathione.
The effectiveness of the antioxidant will depend upon the free radical in the target of damage. Vitamin C will often stop chain reactions because it captures the free radical and neutralizes it. Flavanoids are the biggest class of antioxidants and researchers have identified over 5000 different chemicals in a variety of foods.
Another class of antioxidants are polyphenols, which scientists may refer to as phenols. These are a group of chemical substances found in plants and often found in berries, tea, olive oil, chocolates, peanuts and other fruits.
The Food and Drug Administration recommends that an individual consumes 3000 units of Oxygen Radical Absorbance Capacity per day, a way of measuring the amount of antioxidants found in your food. For example, 100 g of blueberries contains 2400 units and 100 g of spinach contains 1230 units. It is quite easy to consume the recommended amount daily by simply eating a diet full of fruits and vegetables. These antioxidants can then get to work to help to stabilize free radicals which have been linked to chronic diseases such as cancer, cardiovascular disease and immune mediated diseases such as diabetes and lupus.
| Advertisement | |
 |
|

Leave a Reply